SORTING
is needed to speed up searching operation.There are 2 types of sorting based on the final condition of the data: Ascending and Descending.
Sorting also can be divided into 2 types of sort based on their difficulties.
1. Simple Sort : Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, and Insertion Sort.
2. Intermediate Sort : Quick Sort and Merge Sort.
Here I'm going to explain a little bit about my understanding in types of Sorting:
1. Bubble sort : compares 2 variables that are next to each other, swap if certain condition are met, until the end if the data.

2. Selection sort : compares 2 variables, starts from the first element to the second. After that, it compares the first element to the third, and so on. If certain condition are met, it will do a swap between the variables.
3. Insertion sort : has the same principle as having a temporary container to store certain data that is going to be swapped.
4. Quick Sort : it has a kind of 'recursive' scheme to execute this sorting type.
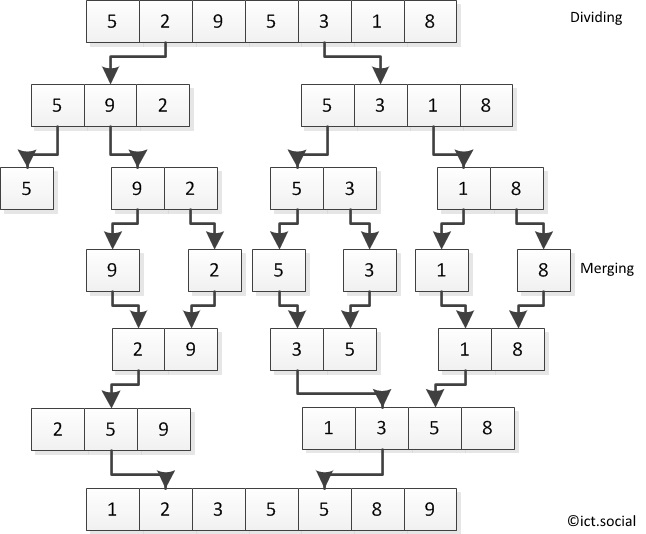
5. Merge Sort : based on 'divide-and-conquer" algorithm. Divide means we divide the data into 2 groups, then we solve each of the problems in the subsets, and lastly, we combine both solutions from each subsets, into one final solution.
SEARCHING
is needed to find certain data or element that is stored in a large array, and then to retrieve the data itself. We need to determine the key value to simplify the searching activity through our data. KEY must be unique for each data in a particular data lists or array.For example, every employer have their own ID number, name, gender, address, date of birth, etc. But the unique value from each of them that is different from the other is their ID number. Thus, ID number can be used as a key when we do searching there.
There are some types of searching:
1. Linear search : compares each element of the array to the key.
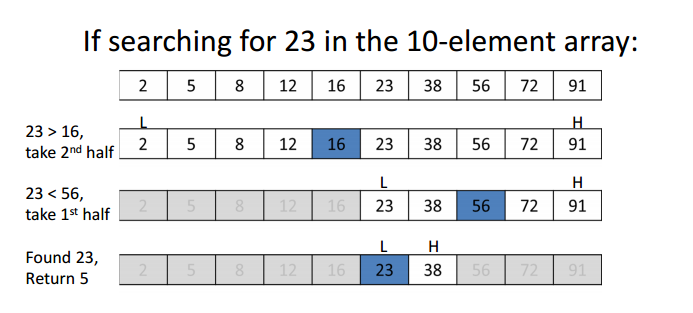
2. Binary search : we divide the data into 2 groups from the middle.
3. Interpolation search : split and look for approximate location of the data.
The formula is :
key - data[min]
Mid = --------------------------- x (max-min) + min
data[max] - data[min]